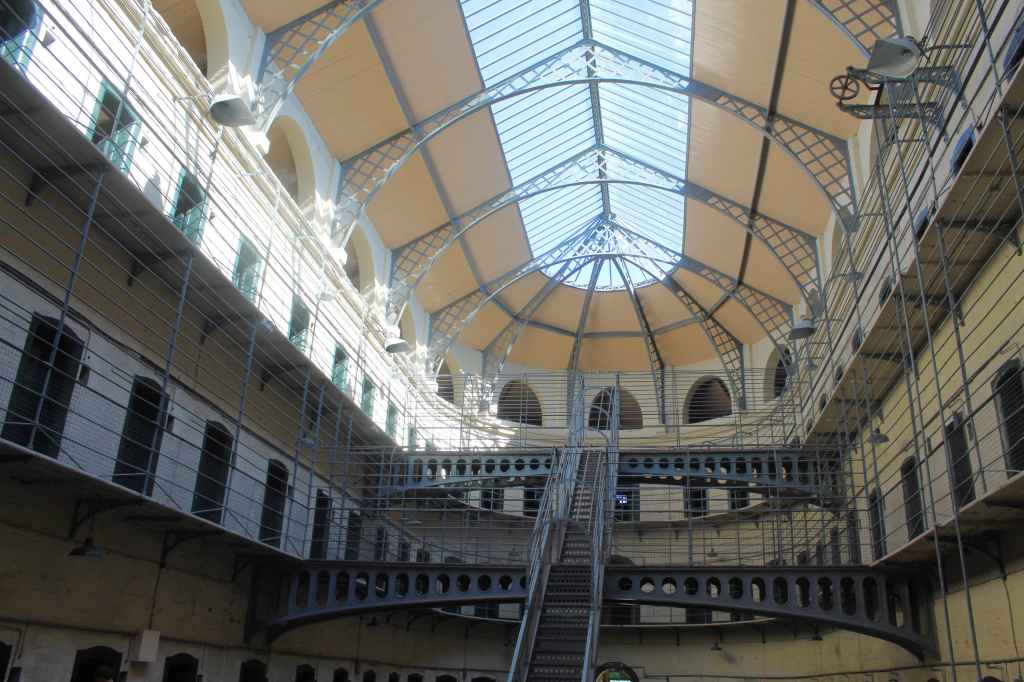
This was the moment of truth. I got into the driver’s seat, put on my seatbelt, and gripped the wheel. I had been nervous about this for months: Could I really drive on the “wrong” side?
My panic didn’t seem unwarranted. After all, I am not the most confident driver in a “normal” car, on the right side of the street. Driving in the mirror image world of Ireland struck me as courting death. All of my instincts would be exactly wrong. And Ireland, with its narrow country roads, is not known as the easiest place to drive.
Nervously, cautiously, I rolled the car from its parking spot and onto the road. It was terrifying at first—especially the traffic circles which travel clockwise rather than counter-clockwise—but by the time I got onto the highway, I felt as though I had the hang of it. And not a moment too soon, for we had a guided tour to catch.
Brú na Bóinne
Virtually everyone knows about Stonehenge, those mysterious rocks in the English countryside. But Ireland has her own neolithic ruins, and they deserve to be just as famous.
We parked the car and walked into the cavernous visitor center. There, we were given time to walk through the informative exhibit, which goes through the basics of what we know about this archaeological site.
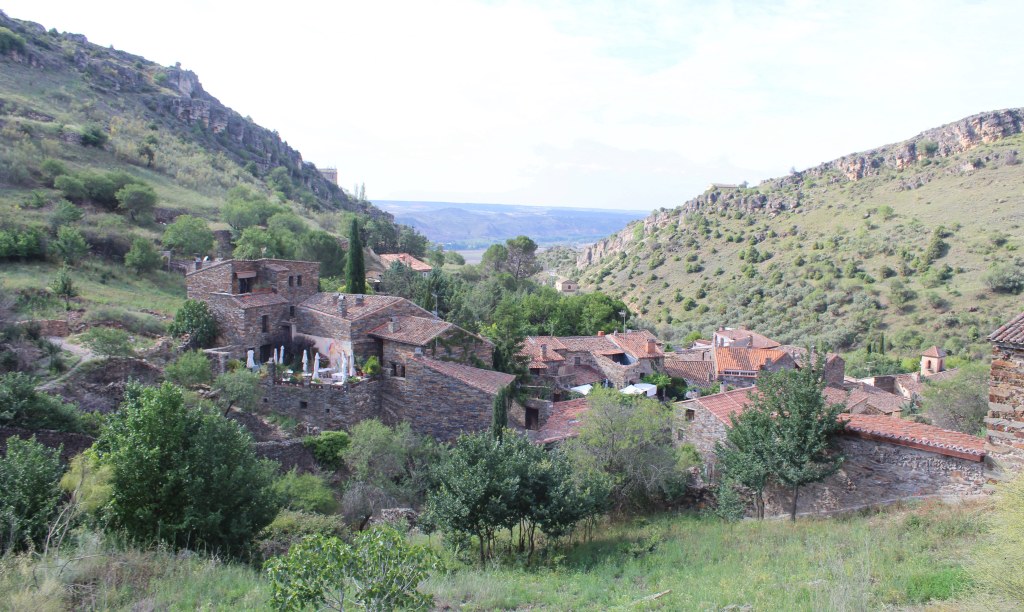
Brú na Bóinne is not a single monument but a whole landscape of ruins. Predating the Great Pyramid by several centuries, it consists of a complex of stone and earth structures, ranging from decorated megaliths to elaborate passage tombs. Like Stonehenge, the site incorporates enormous stones, many of which were transported from far away; and, like Stonehenge, several features of these tombs are aligned with astronomical events, such as the winter solstice. The people who built these tombs were obviously quite sophisticated.
After about half an hour, we were summoned for the real start to the tour. To get to the buses, we had to cross a pedestrian bridge that spans the River Boyne. It was a beautiful day, unseasonably warm for September, and this was our first real glance of the Irish countryside. Although the landscape now must be very different from how it was so many years ago, it was easy to see what attracted the builders of these monuments to this spot. The land was bursting with life.
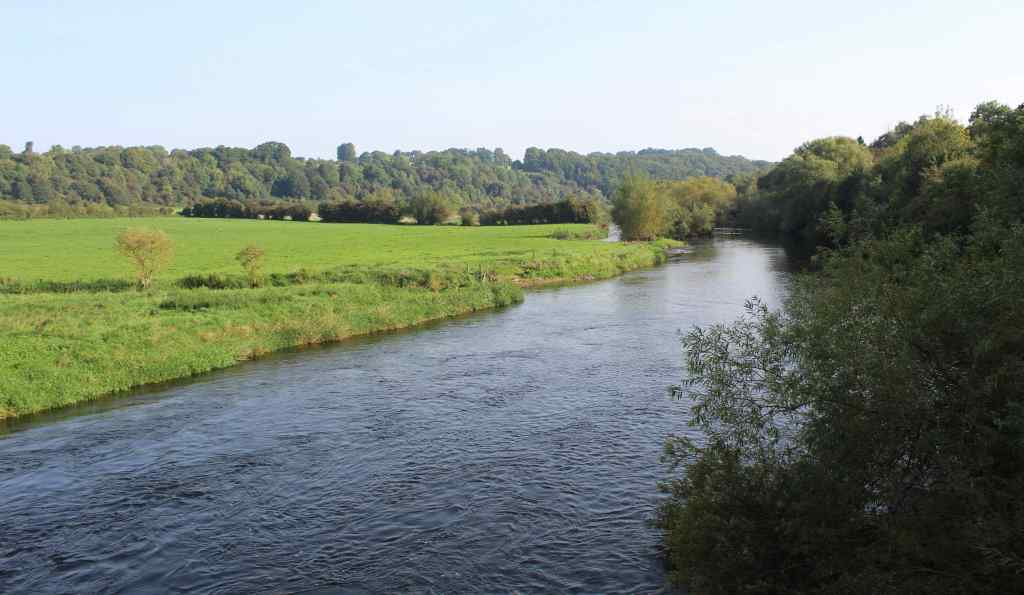

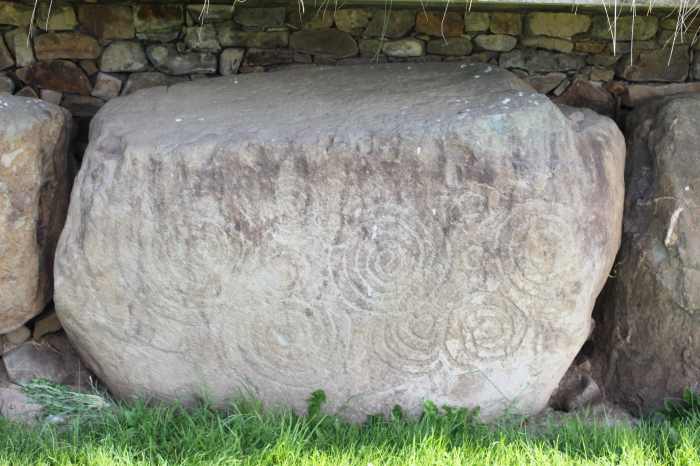
Small buses ferried us the short distance to our first stop, Knowth. This is an assemblage of artificial mounds—piles of earth ringed with decorated stones. These carved kerbstones represent one of the most important collections of prehistoric art in Europe, and they are remarkable indeed. The art is stylized and mostly abstract, consisting of swirling patterns that have been emulated far and wide.
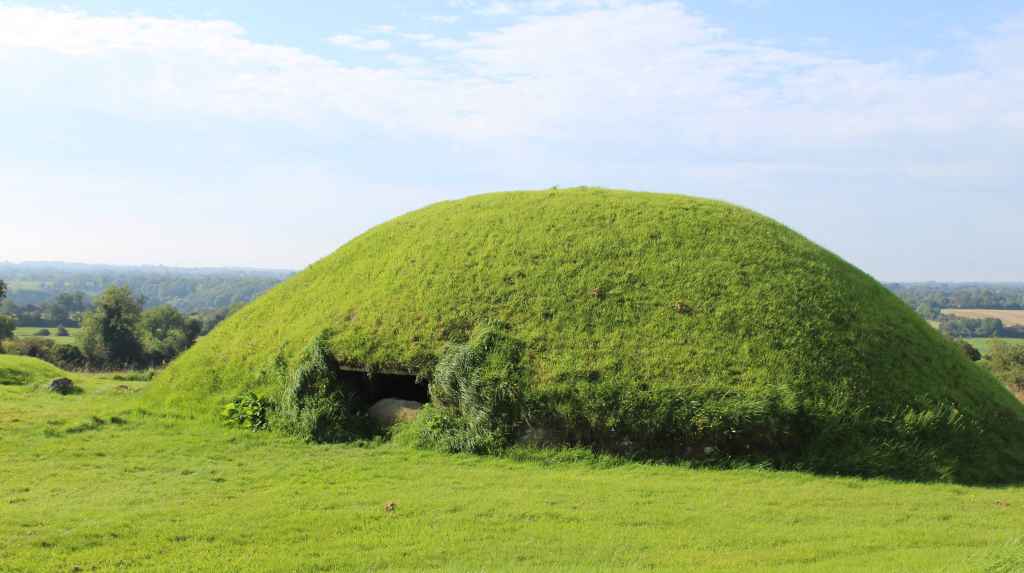

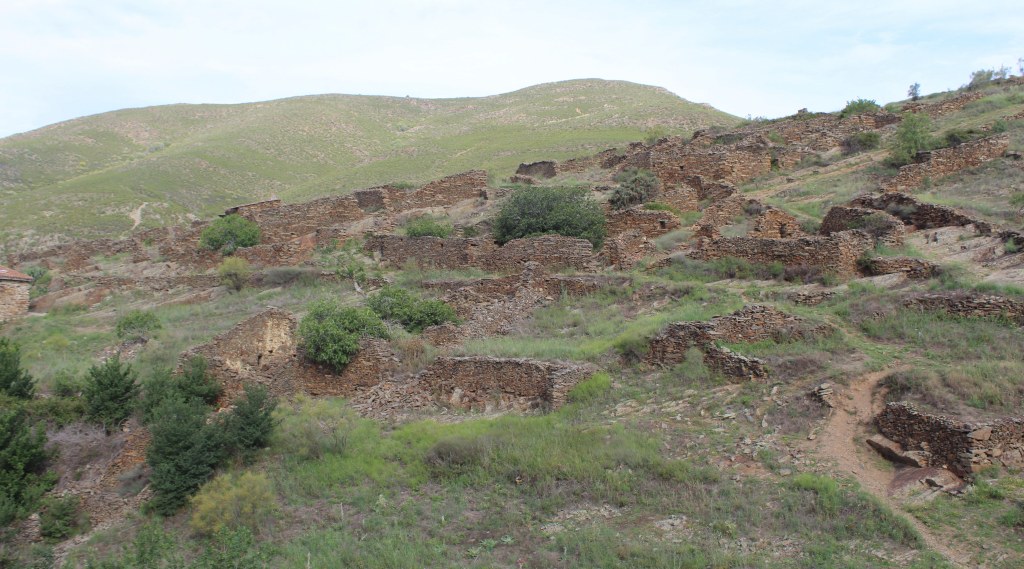
Walking through the site, the visitor is immersed in a whole artificial landscape. The bulbous green mounds are imposing and mysterious. Each one was a tomb. But who were these people? And what did they believe? Whoever they were, they obviously lived in a society with a great degree of sophistication and coordination, as the main passage tomb is a major construction. Two passages were dug into the mound, meeting almost exactly in the middle. More impressive still, these passages were made waterproof. Unfortunately, later intervention (the site was continually used and modified through the years) undid this waterproofing, and the passage tomb can no longer be visited.

Knowth is a world-class prehistoric site, but Newgrange is the real showstopper. It is another passage tomb, though instead of being ringed by decorated stones, it has a grand, almost ostentatious facade of white quartz. Standing alone on the top of a hill overlooking the river, the tomb looks uncanny, almost otherworldly. I am no believer in ancient aliens, but I can see how these old monuments, which seem to emerge from the landscape, can be unsettling.
Unlike Knowth, the passage of the tomb at Newgrange is still intact, and so visitors can actually go inside. This was mind-boggling to me. No place I had ever visited even remotely compared with the age of this monument. The Colosseum in Rome is nearly 2,000 years old, the Parthenon in Athens is about 500 years older. Newgrange was built over 2,500 years before that. This means that, by the time the Parthenon was constructed, it was about as old to the ancient Greeks as their own monument is to me.
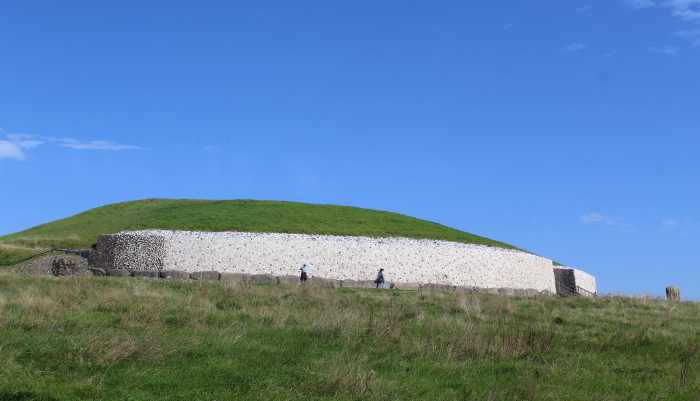

Compared to these other two monuments, however, it may be difficult for the modern visitor to appreciate the sophistication of Newgrange. A mound of grass is simply less stunning than a huge marble column. But it is not at all easy to build a passage like this one. The stones had to be placed in such a way that they could support their own weight, as well as the considerable weight of all the material on top of them—and, all of it had to be properly waterproofed so that it wouldn’t flood during the first rainstorm. This is quite impressive engineering.
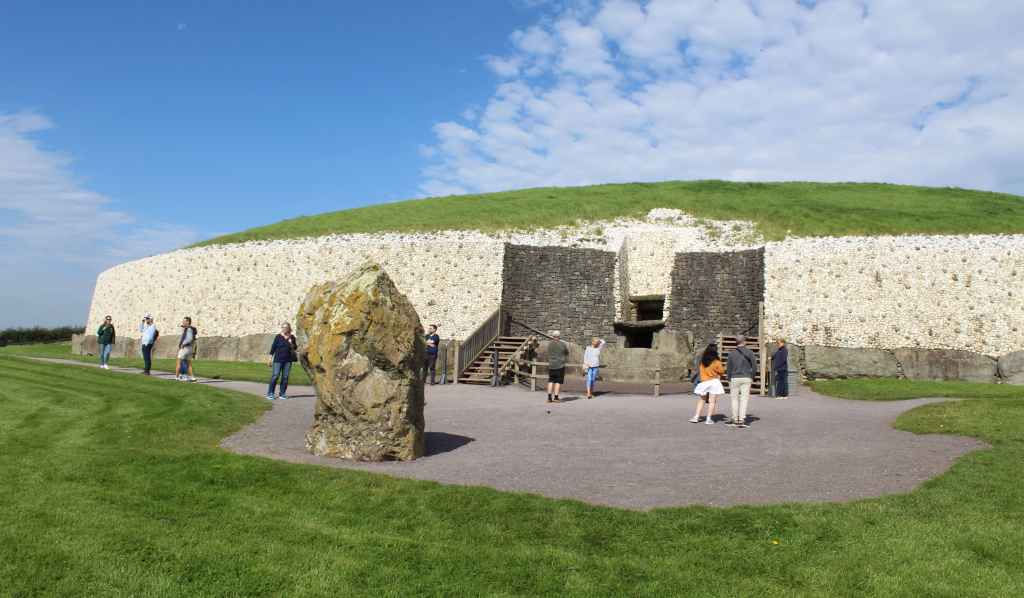

Even to a modern unbeliever like me, there is obvious religious symbolism to the tomb. The walk through the long, dark passageway suggests the path from life to death, and from death to life. This mystical impression is doubly strong when one factors in the “roofbox,” which is the additional opening near the entrance that allows sunlight to enter—but only during a brief moment during the winter solstice.
Since the solstice was still over two months away when we visited, the guide did the next best thing, and activated a light that had been installed near the entrance. First, the overhead lamp dimmed to nothingness, leaving us in darkness. Then, a ray of yellow light creeped through the long passageway until it hit the back of the chamber. Over 5,000 years later, the sight is still awe-inspiring—a testament both to the beauty of the natural world and our own understanding of the cosmos. It would take a heart of stone not to be moved at such a sight.
Glendalough
The car kept brushing against the side hedges and throwing up pebbles as we hugged the side of the road. My brother was driving; and even though this was after a week of practice, he was still nervous.
This was a week later, our last day with the rental car. We were on our way back to Dublin to drop it off. But first, we had a last bit of sightseeing to do.
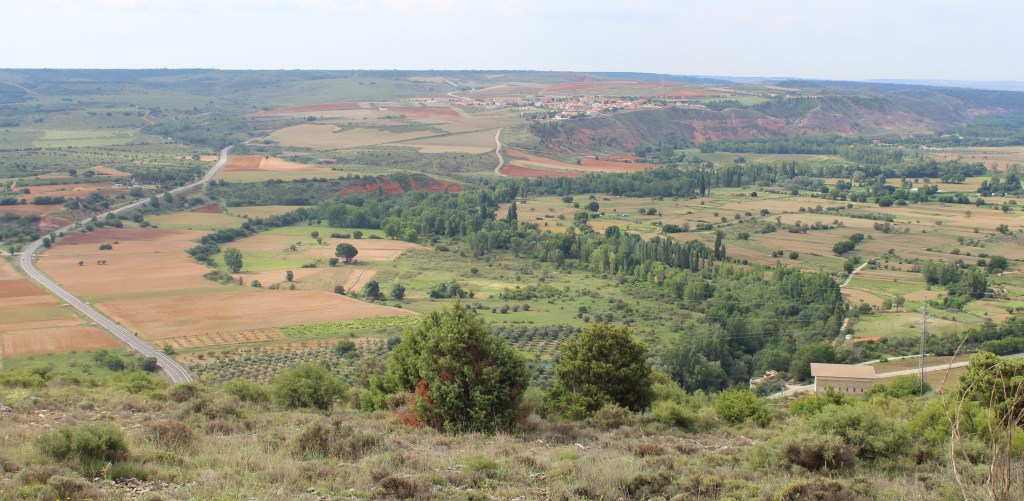
The countryside was, as usual, bucolic. We rolled up and down the green hills, past sheep, tractors, and cottages. At one point, as we rounded a bend, a sign came into view on the hillside above us. It read “Hollywood,” which is exactly where we were: a village in County Wicklow, of about 500 people.
We pressed on. And as we did, the landscape transformed. We were gaining in altitude as we ascended into the Wicklow Mountains. The landscape became rockier, more rugged, and we were treated to an ever-improving sight of the valleys below us.
Soon we pulled into our destination: Glendalough. This is one of the loveliest valleys in the mountain range. Carved out thousands of years ago by a glacier, it later became the site of an important monastery, founded by one St. Kevin. Not much can be said for certain about this saint—there are no contemporary sources about his life, and subsequent generations have thoroughly mythologized him—but it is certain that he at least had a good eye for natural beauty, as he chose a gorgeous spot.
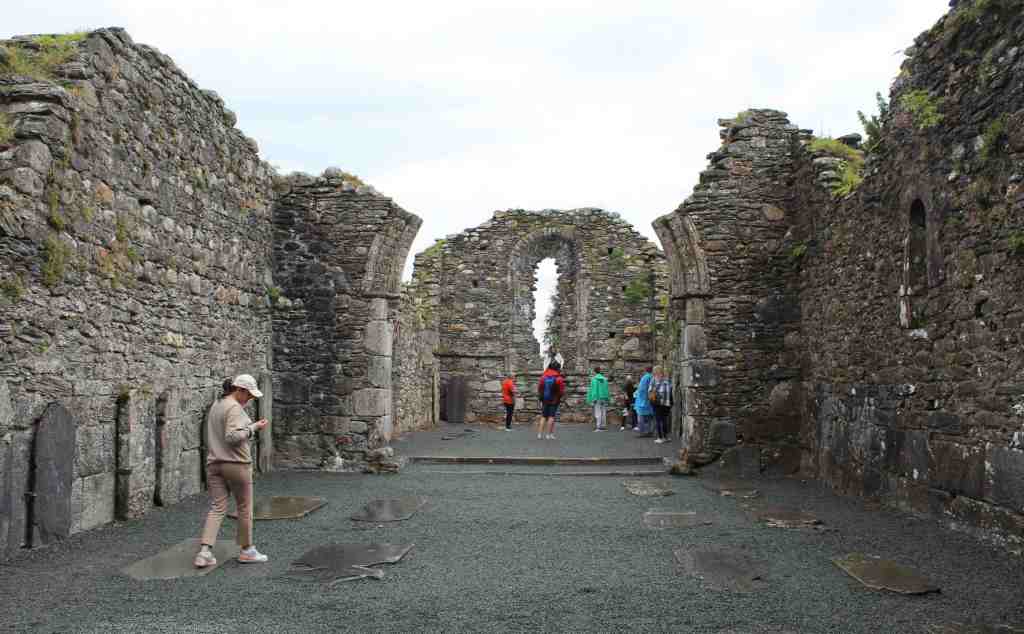

The monastery founded by this saint flourished for several hundreds of years after his death, in 618. However, the English—those dependable villains of Irish history—ransacked the place in 1398, burning much of it down. What remains is just a fraction of the original settlement, a haunting collection of graves, walls, and half-destroyed buildings.
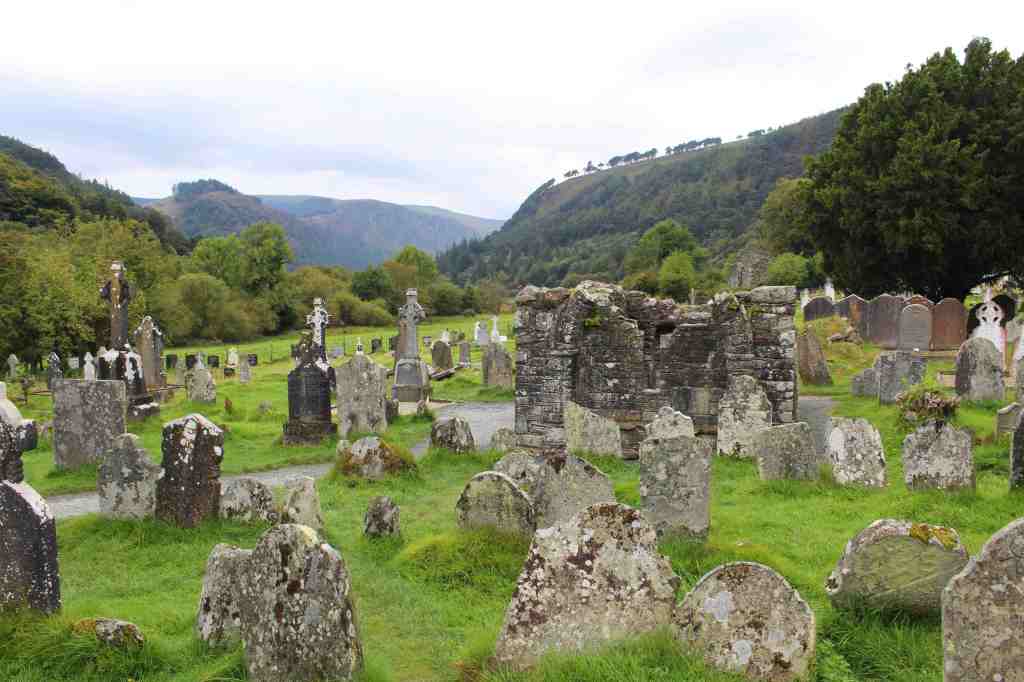

The impression of lost time is somewhat lessened, however, by the hoards of tourists who arrive by the busload. Because of its proximity to Dublin, you see, Glendalough is a very popular destination for day-trippers, and the place now has all the trappings of mass-tourism. Parking attendants frantically direct traffic in and out of the many parking lots, while rows of food stands sell burgers and fries to visitors. It is an ironic fate for a place that St. Kevin must have chosen for its peacefulness.
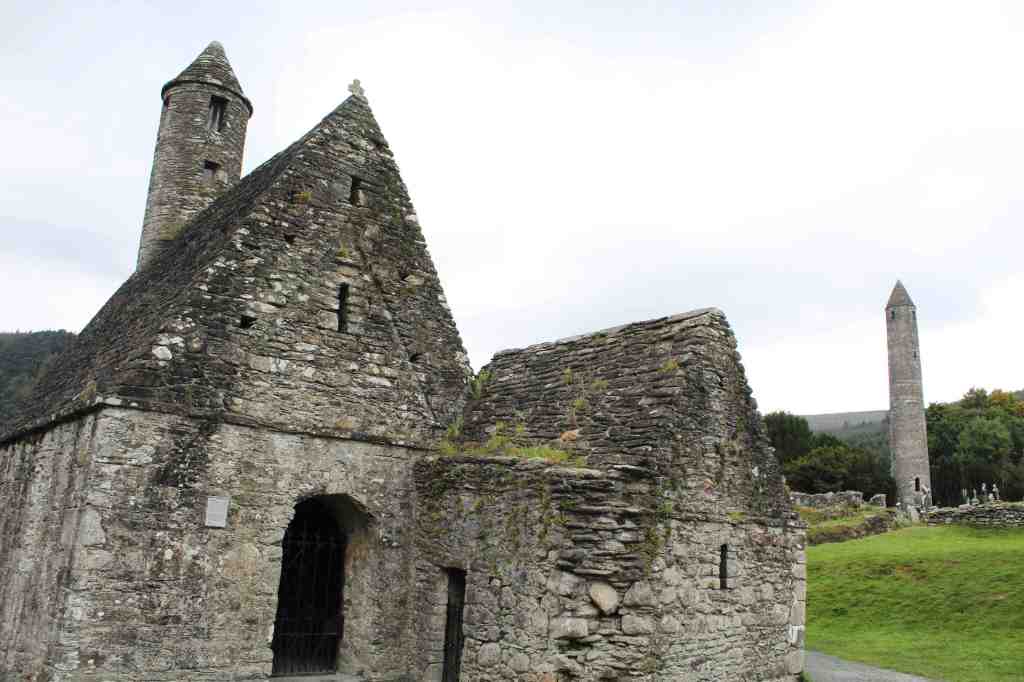

When we visited, conditions were unfortunately not ideal to fully appreciate Glendalough. For one, we were short on time; and the weather was turning dark and stormy. If I’d had more time, I would have loved to do more hiking in the valley, and perhaps visited the Miner’s Village, where workers in the local lead mine used to live. That will have to wait for my next visit.
As it was, after just a couple of hours in Glendalough, we got back into our car and drove the remaining hour to Dublin. Now it was my turn to drive—one last stretch of stress and terror on the roads of Ireland. But fortune was on our side, and we made the journey without a significant mishap. It was with a great sigh of relief that I shut the door of the car and handed the key to the attendant. The crisis had been averted. We had avoided becoming yet another Irish ruin.